Green Power Market: Driving the Future of Sustainable Energy
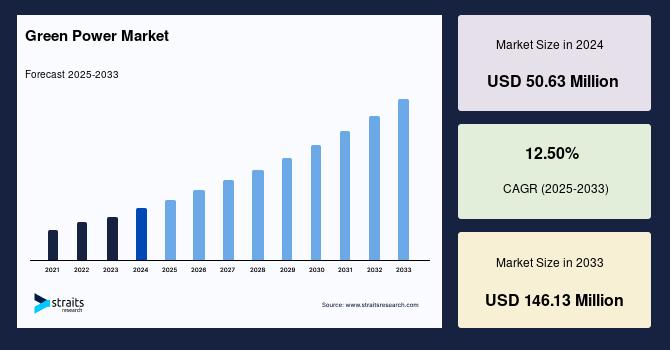
The global green power market size was valued at USD 50.63 million in 2024 and is projected to reach from USD 56.95 million in 2025 to USD 146.13 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12.50% during the forecast period (2025-2033). This rapid growth is propelled by increasing investments in green power projects, growing energy demand across industrial and residential sectors, and stringent global regulations targeting carbon emissions reduction amidst climate change concerns.
Market Dynamics and Key Drivers
Green power, often interchangeably called clean energy, refers to electricity and mechanical energy generated from renewable resources such as wind, solar, hydro, biomass, geothermal, and waste energy. Its defining characteristic is minimal to no harmful environmental impact during production, making it crucial in combating global warming and reducing greenhouse gases.
The transition to green energy is encouraged by the volatility and environmental toll of fossil fuels, combined with government mandates worldwide to meet sustainability targets. The burgeoning market for electric vehicles (EVs) also spurs the green power sector, as cleaner energy is essential for sustainable transportation electrification. However, high initial infrastructure costs for green energy projects present growth challenges, requiring significant capital investment and long development cycles.
Regional Market Insights
Asia-Pacific emerges as the fastest-growing region in the green power market, driven primarily by China and India’s rapid industrialization, population growth, and escalating energy needs. Both household and industrial sectors in these countries increasingly prioritize renewable sources due to improved affordability and supportive government policies. Although India historically exhibited slower green power adoption due to inconsistent economic policies, recent financial backing for renewable projects signals a future surge.
Europe holds the position of the largest market for green power globally. Countries like Germany lead in installed wind capacity and overall investment in renewable infrastructure. European initiatives promoting renewable targets have pushed several nations, including Denmark, Sweden, and Scotland, to generate substantial shares of their energy from green sources.
In North America, the United States dominates green power production, exporting surplus energy to neighboring countries like Mexico. Canada also contributes significantly, with notable government incentives fueling investment in clean technologies and renewable infrastructure. Meanwhile, Latin American, Middle Eastern, and African regions experience moderate growth fueled by increasing government partnerships aimed at sustainability.
Green Power Source Segmentation
The green power market is composed of several key renewable energy sources, each with unique characteristics and applications.
-
Wind Power: The leading contributor to the green power market, wind energy is abundant, cost-effective, and rapidly deployable. Regions with consistent wind patterns optimize this resource for electricity generation. Europe dominates in revenue from wind power due to extensive installed capacity, while Asia-Pacific leads in volume.
-
Solar Power: Utilizing solar radiation through photovoltaic cells or solar thermal systems, solar energy markets are expanding swiftly, especially in residential and commercial sectors across Asia-Pacific. Declining solar panel costs and heightened infrastructure adoption enhance its appeal.
-
Hydropower: Harnessing the kinetic energy of flowing or falling water, hydropower is a major green energy contributor. Low-impact hydro projects producing up to 25 MW nearby Colombia and Peru show how hydropower can provide clean, efficient electricity with minimal environmental disruption.
-
Biomass and Bioenergy: Derived from organic matter like plants, wood, and waste, biomass offers renewable electricity and is particularly prominent in European markets. Governmental incentives further promote bioenergy development.
-
Others: This category includes geothermal energy and waste-to-energy technologies. Geothermal exploits earth’s internal heat, prevalent in countries with geothermal reserves. Waste-to-energy systems are increasingly valued for both environmental benefits and economic viability, with successful implementations in the U.S. and parts of Asia.
Market Applications by End Use
Green power applications span several domains:
-
Buildings Sector: Residential and commercial buildings represent the highest green power consumers. Technologies include solar thermal systems, geothermal heat pumps, biomass heating, and wind turbines integrated into building energy systems. Rising populations and urbanization in Asia-Pacific amplify energy demand in household and commercial infrastructures.
-
Industrial Sector: Industries like food processing, chemical manufacturing, and metal production increasingly adopt green power for steam generation, process heating/cooling, and electricity needs. Rapid industrialization in developing regions fuels consumption growth.
-
Transportation: The transport sector’s growing adoption of electric and hydrogen-powered vehicles contributes to green power demand. Increasing mobility, tourism expansion, and governmental pushes to reduce carbon emissions intensify requirements for clean energy in passenger and commercial transportation.
-
Non-Combusted Applications: This emerging segment covers feedstock uses in petrochemicals, lubricants, and related industries, which utilize green energy instead of fossil fuels. Rising pressure on petrochemical producers to lower carbon footprints underpins growth in this area.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While green power markets enjoy robust expansion, certain hurdles remain. High upfront costs of renewable infrastructure ranging from site monitoring and resource assessment to specialized training and installation pose investment challenges. Additionally, intermittency concerns associated with solar and wind resources necessitate parallel advancements in energy storage and smart grid technologies.
Government policy remains a pivotal factor, with community choice aggregation models and subsidies helping spread access to green energy sources. Collaborative public-private projects and cross-border electricity trading also support market expansion.
Looking forward, increasingly affordable technology, rising energy needs, and advocacy for a carbon-neutral future position green power as a cornerstone of global energy production. The anticipated growth in hybrid renewable systems, combining multiple energy sources with battery storage, promises enhanced stability and efficiency. Moreover, rising environmental awareness among consumers and corporate sectors drives demand for clean power alternatives.
In conclusion, as nations forge pathways to sustainable development and climate resilience, the green power market stands out as a critical enabler of environmental protection, economic growth, and energy security. Its continued evolution and adoption will be integral to meeting future global energy demands while preserving the planet for generations to come.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


